If you think your game suffers tremendeously from App Store Piracy, you’re wrong. To put it bluntly: your game has simply failed on the market!
Reports that put the App Store piracy rates at “at least 60%” and developers reporting piracy rates of 80% and even up to 95% are mathematically correct but what they often forget to tell you are actual sales numbers. In the rare cases where Indie developers also mention how many sales they have made, pirates or not, these numbers are always extremely low. For a commercial developer who reports an 80% piracy rate on one of his games it’s simply an attempt to turn terrible sales into a PR story which might give their game a little bit more attention. In fact, i expect the games who report piracy rates of over 30% to have sold no more than 5,000 copies. At $.99 this creates a revenue of $3,500 - maybe a good number for a two-man team but a catastrophe for a commercial developer. This is hardly a problem caused by piracy but a simple failure of the product on the market.
What you have to understand about Software Pirates in general: they use a lot of software. In fact, this is their hobby and favorite passtime, to try out as much software as they can get their hands on. So you will always have a minimum amount of pirated copies of each piece of software, no matter how successful this software is (or not). Of course, with higher success and more sales of the software more pirates are also likely to use it because they, too, value quality software. But given the amount of jailbroken iPhone devices prepared to run pirated software there’s a hard cap of the maximum amount of piracy you will ever see on any title. Just as much as there will be a minimum number of pirates playing every game as soon as it becomes available and regardless of how successful it is on the App Store. If your sales are close or below that minimum number of pirates, you naturally get piracy rates of over 50%. These pirates don’t cut into your revenue however. Ignore them. They never would have bought your App in the first place!

David Rosen from Wolfire reports in his Another View on Piracy article that the highest number of Jailbroken iPhones worldwide is said to be 10%, and in the USA - whose users constitute about two thirds of the iPhone/iPod market - the number of jailbroken devices is just 5%. Assuming a total installed base of 75 Million iPhones (50 Mio. as of April 2010) and iPod touches (20 Mio. as of Sept. 2009) we get at most 7.5 Mio jailbroken devices worldwide, or approximately 2.5 Mio jailbroken devices in the USA. They are not all pirates, however. PinchMedia reports that 38% of jailbroken devices have run at least one pirated App. They also state this number is low. So let’s just take half and we’ll end up with 3.75 Mio. jailbroken devices worldwide which have run at least one pirated App. Still a pretty high number - but it only tells us that they have started one pirated App but not how many or how much of a pirate these users really are. If i had to guess i would say that 10% or just about 400,000 of these users are active pirates who try out a lot of Apps on an almost daily basis. These are the pirates who make the biggest impact in terms of per-App piracy numbers. They are also the users who are least likely to upgrade their pirated copy to a legal one, if they ever do it at all. And trying to fight these pirates is anything but futile - they will never be your customers!
PinchMedia also supports my theory that most Pirates try out as much Software as they can which, of course, leaves less time to use each App intensely: “Pirated applications are used less frequently, less intensely, and for a shorter overall length of time than purchased applications.”
Let’s go back to the gist of it: developers who have a problem with App Store Piracy have, in my opinion, either a problem of perception or they’re making a simple PR statement aimed at getting them more attention, hoping to achieve better sales. The developers who suffer most from App Store Piracy are those who simply are not successful. Their real problem isn’t Piracy, it’s much more likely that they failed either at Marketing, Timing, Quality or finding their Target Audience.
Let me sum this up with a simple chart which i think explains why App Store developers report amazingly high piracy rates, when in fact they are reporting the commercial failure of their App:




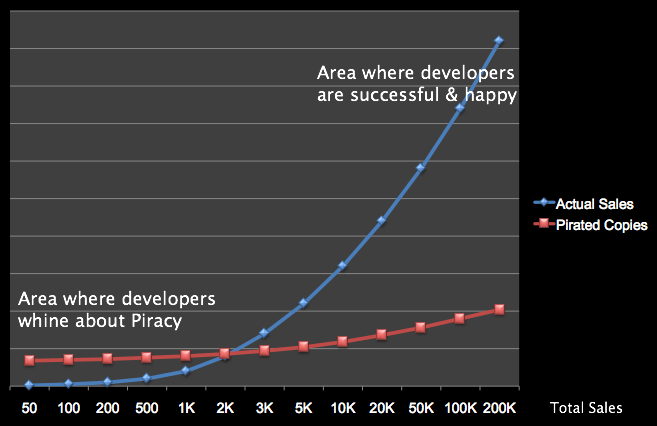








Bad user reviews and comments can actually be a good thing
Bad reviews, or simply trash talking and bad-mouthing, can have a positive effect on your game, and yourself. Don’t be overly concerned if some idiots voice their BS and drag down your review score. If you value what you do and others see that value, the positive effect of some bad rep is simply that it encourages others to voice their opinion in favor of the product and you. The things you should not do, however, is to be overly protective and try to remove such posts. That will only serve to earn you disrespect from everyone because freedom of speech is a much higher value. If disrespected, it will earn you much more disrespect in return. If you’re in doubt whether what’s been said is offensive, keep it online until someone complains. The more absurd and unreasonable negative comments are the more happier should be, and you’ll quickly notice other users jumping in to make their case. You, on the other hand, should stay out of it. React to the positive comments, ignore the bad-mouthing and trash-talking that is only targeted to lure you out in the open.
Applied to the App Store, where you have no control over the bad reviews other than complaining about them in your blog: don’t do it. No one cares about your whining on bad reviews. They happen. If your game is really good, it will get good reviews. The bad ones will only serve to encourage others to post their opinion and they often provide good reasons not to listen to “those jerks”. The other bad reviews which are clearly not from idiots you should hold dearly. They contain valuable criticism about your product. It will help you improve. Nothing is more powerful than a dissatisfied customer or someone who was simply disappointed which you were able to turn to your side by listening and reacting to their criticism. People love to criticize, but even more so they love when someone is actually listening and making changes in their favor.
Caveat: some people will always criticize no matter what. And some will always know how to make things even better. Those are the kind of people who could sway you into feature-creep, don’t listen to them, they’ll kill your product the more you try to make it theirs. And some will be jerks for live and just randomly change their opinions on a daily basis, probably based on what they heard or read today, or whether they were drinking or not, or whether today’s weather is good or bad. Listen only to the feedback that is voiced most often, which others agree on and which is consistent.